A CNC machine (short for Computer Numerical Control machine) is a type of machine tool that is operated by a computer. These machines use a series of pre-programmed instructions to guide the cutting, shaping, and drilling of materials such as metal, plastic, and wood. CNC machines are highly accurate and efficient, and they can produce complex parts and components with very tight tolerances.
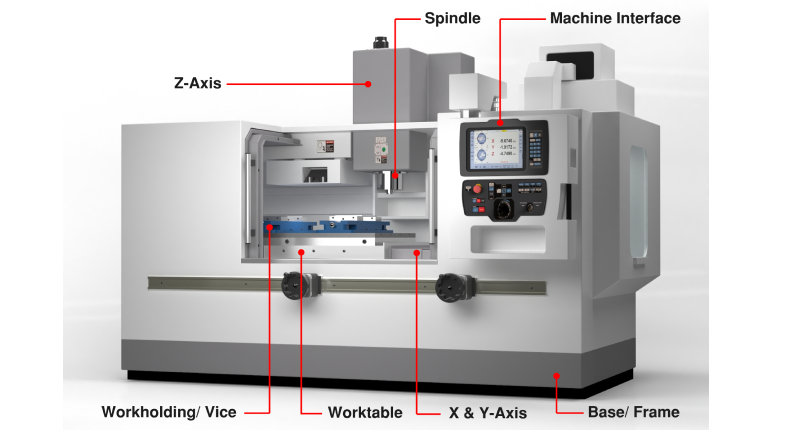
The basic components of a CNC machine include a cutting tool, a workpiece, and a series of motors and controls that move the tool and workpiece in a precise, coordinated manner. The cutting tool is typically a rotating bit or end mill, and the workpiece is typically clamped in place on a table or fixture. The CNC machine is programmed using software that allows the operator to specify the dimensions, shape, and other parameters of the part to be produced. Once the program is loaded, the machine can work autonomously, cutting and shaping the material according to the programmed instructions.

CNC machines are used in a wide range of applications across various industries due to their high precision, accuracy, and efficiency.
Some of the most common applications of CNC machines are:
Manufacturing: CNC machines are extensively used in the manufacturing industry for producing complex parts and components with high precision and accuracy. CNC machines are used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices for manufacturing parts such as engine components, gears, casings, and implants.

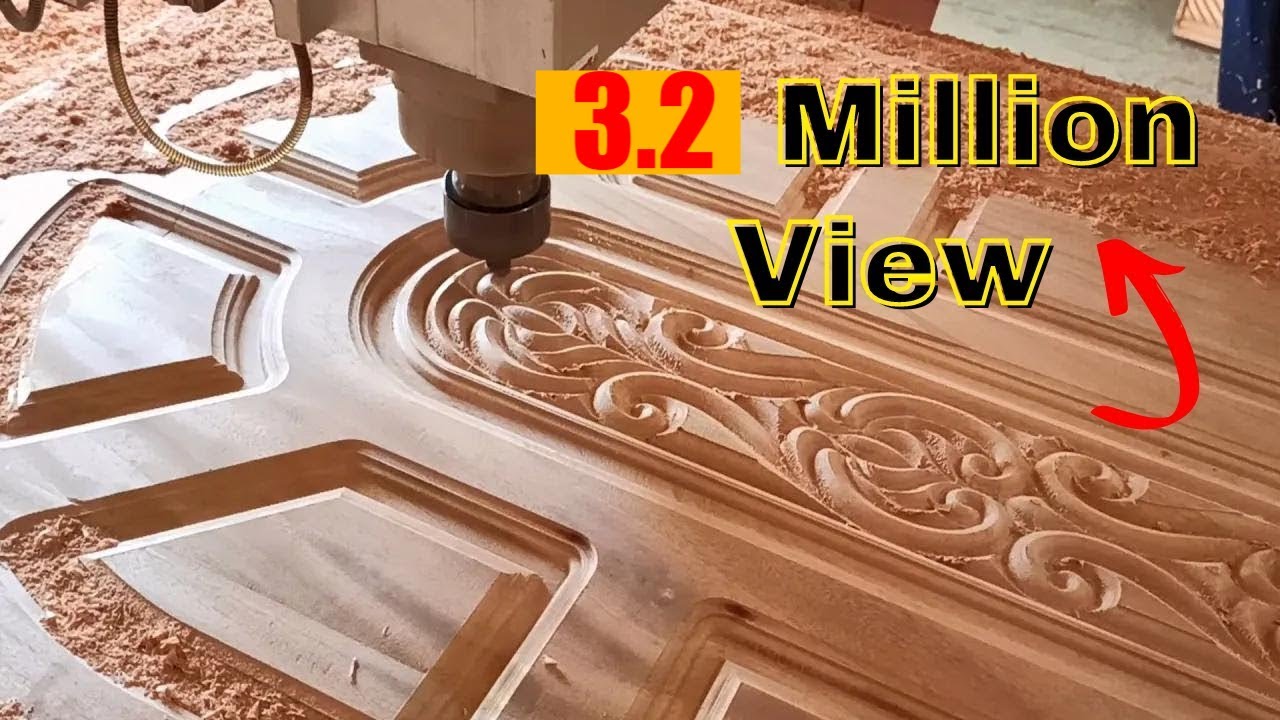
Woodworking: CNC machines are used in the woodworking industry for cutting, carving, and engraving wood. These machines are used to produce furniture, cabinetry, musical instruments, and decorative items with intricate designs.

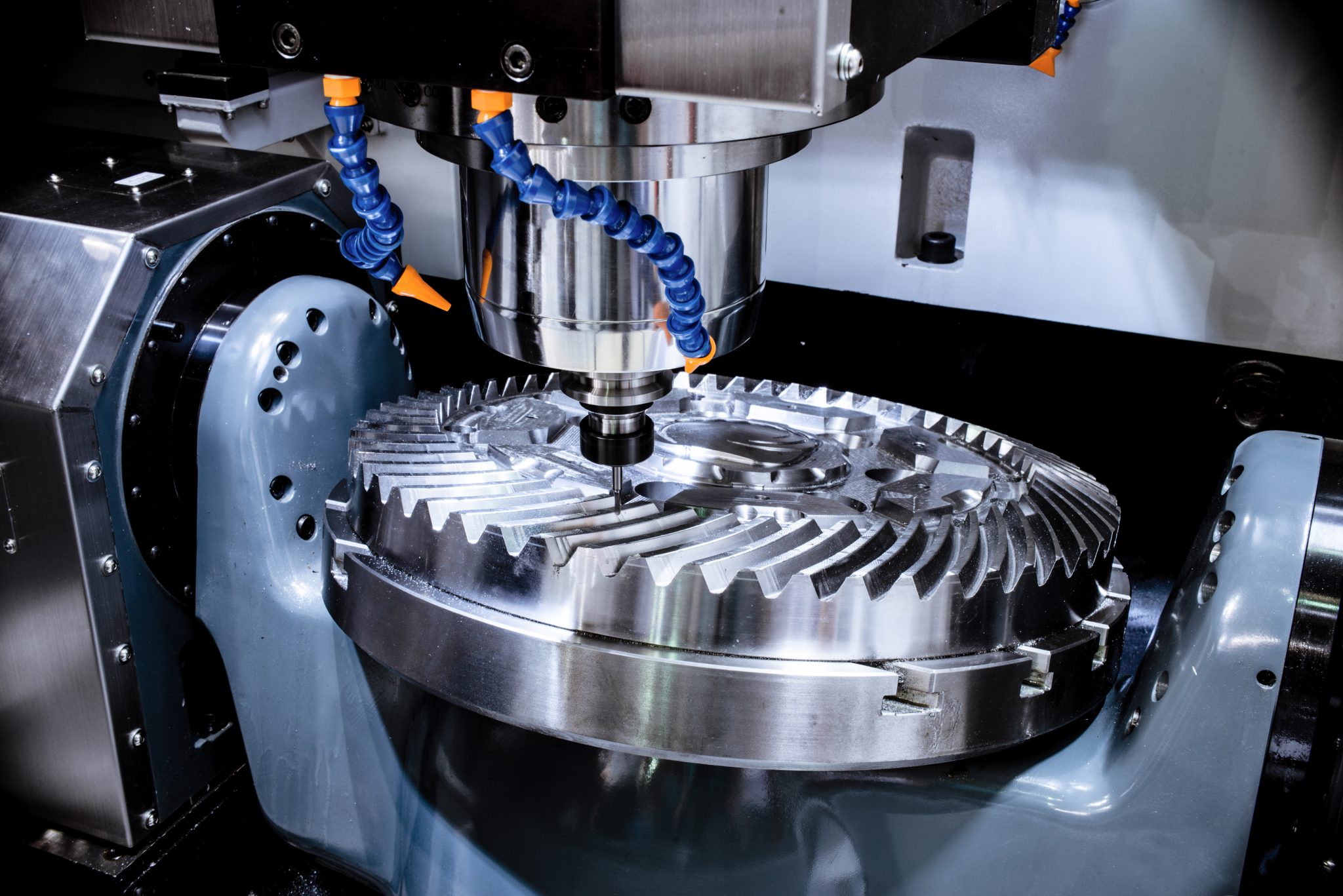
Metalworking: CNC machines are used in the metalworking industry for cutting, drilling, and shaping metal. They are used for producing parts such as gears, shafts, and metal casings.
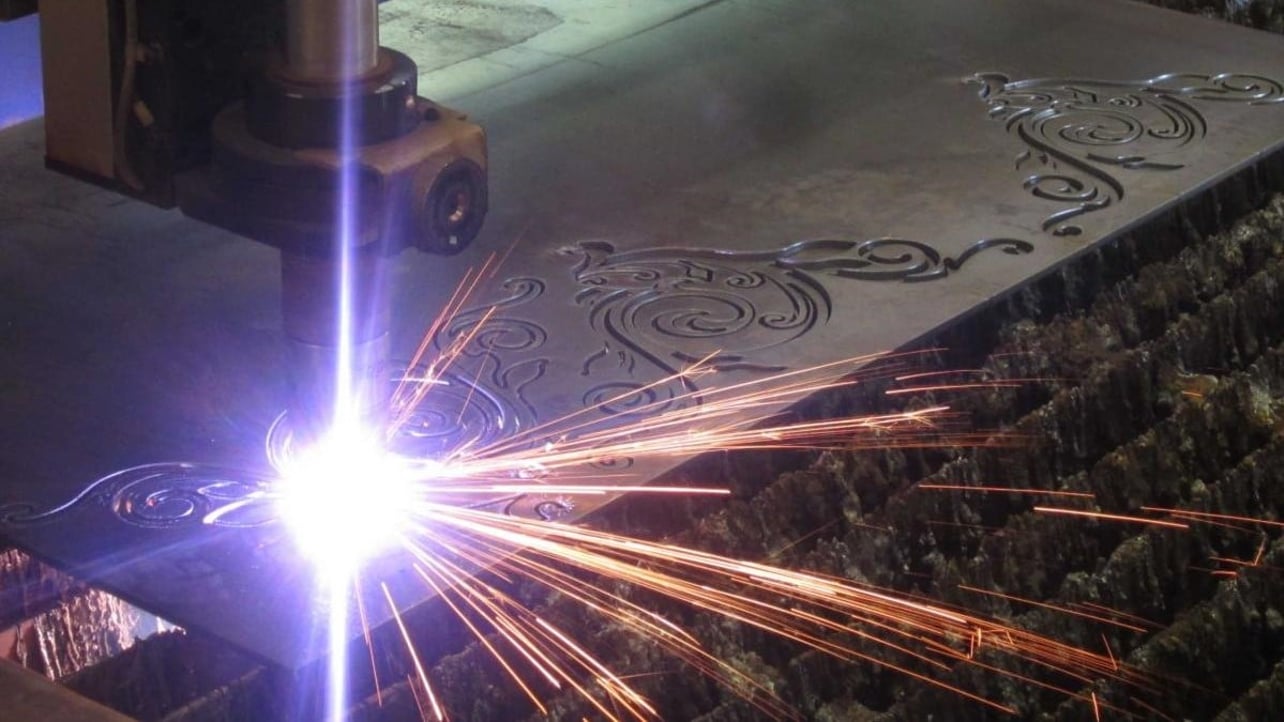

3D printing: CNC machines are used in the field of 3D printing to create parts and objects from various materials such as plastics, metals, and ceramics. These machines use computer programs to create three-dimensional objects from digital designs.
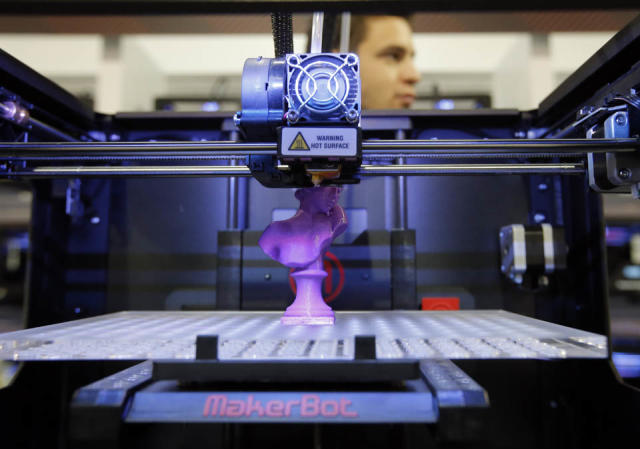

Prototyping: CNC machines are used for creating prototypes of new products and components. The high precision and accuracy of CNC machines make them ideal for creating prototypes that are identical to the final product.

Artistic creations: CNC machines are used by artists and designers to create unique artistic creations such as sculptures, engravings, and jewelry. These machines are used to create complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce by hand.
While there are many advantages to using CNC, such as increased accuracy and efficiency, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Some of the main disadvantages of CNC include:
High initial investment: The cost of purchasing and setting up CNC machines can be quite high, which may not be feasible for small businesses or individual hobbyists.
Complexity: CNC machines are complex and require skilled operators to set up and run them effectively. This can be a challenge for businesses that don't have experienced technicians on staff.
Limited flexibility: CNC machines are designed to perform specific tasks, so they may not be as versatile as manual machines that can be adapted to a wider range of applications.
Maintenance and repair costs: CNC machines require regular maintenance and may need costly repairs if they break down. This can add to the overall cost of operating the machines.
Dependence on electricity: CNC machines rely on electricity to function, which means that power outages or other electrical issues can disrupt production and cause downtime.
Limited human input: While CNC machines can improve efficiency, they also remove the human touch from the manufacturing process, which can be a disadvantage in some industries where customization or personalization is important.
Risk of programming errors: CNC machines are controlled by computer programs, and errors in programming can lead to costly mistakes or even safety hazards.
Overall, while CNC machines have many advantages, it's important to consider the potential drawbacks before investing in this technology

